2016 Toyota Prius
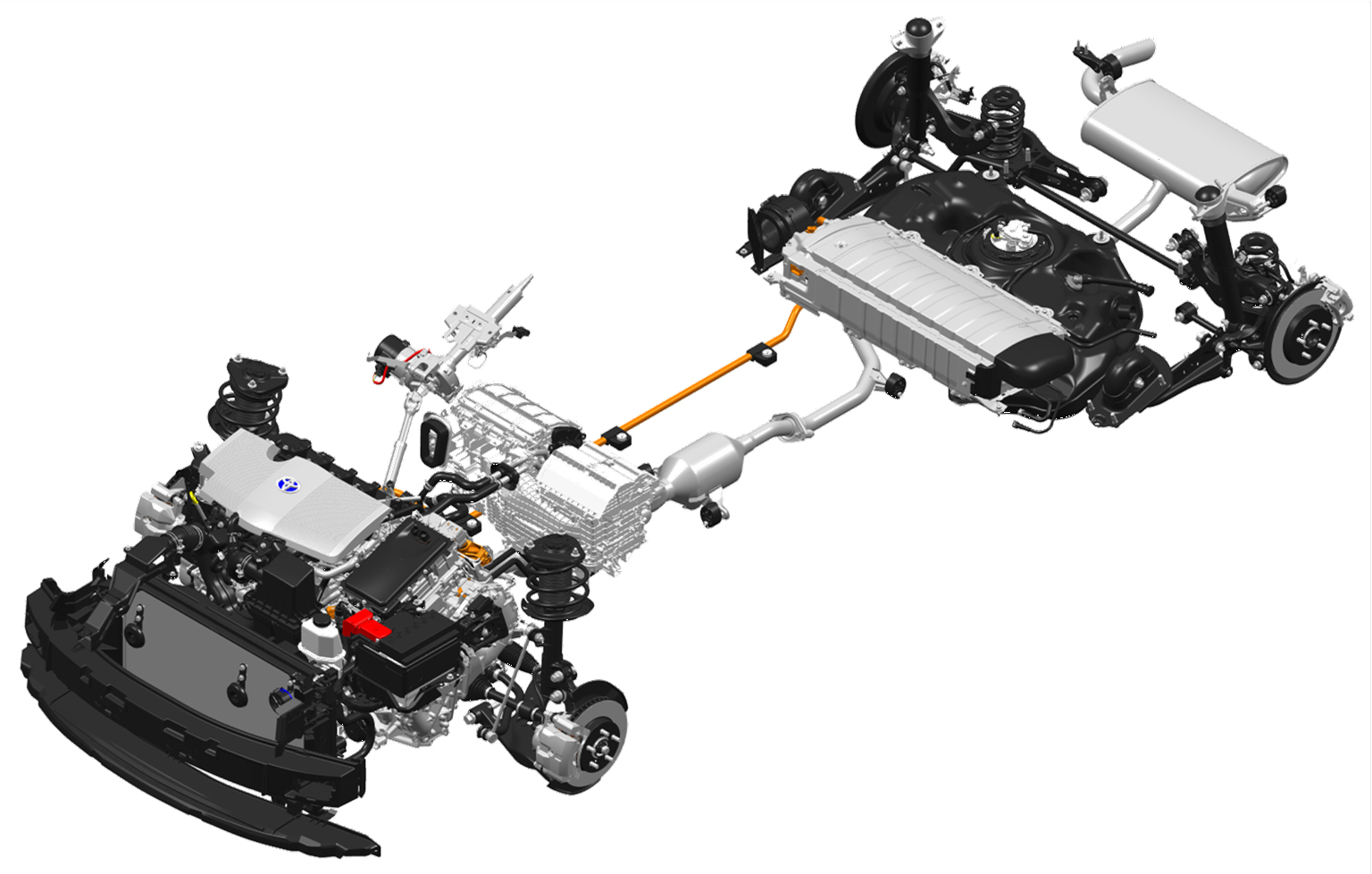
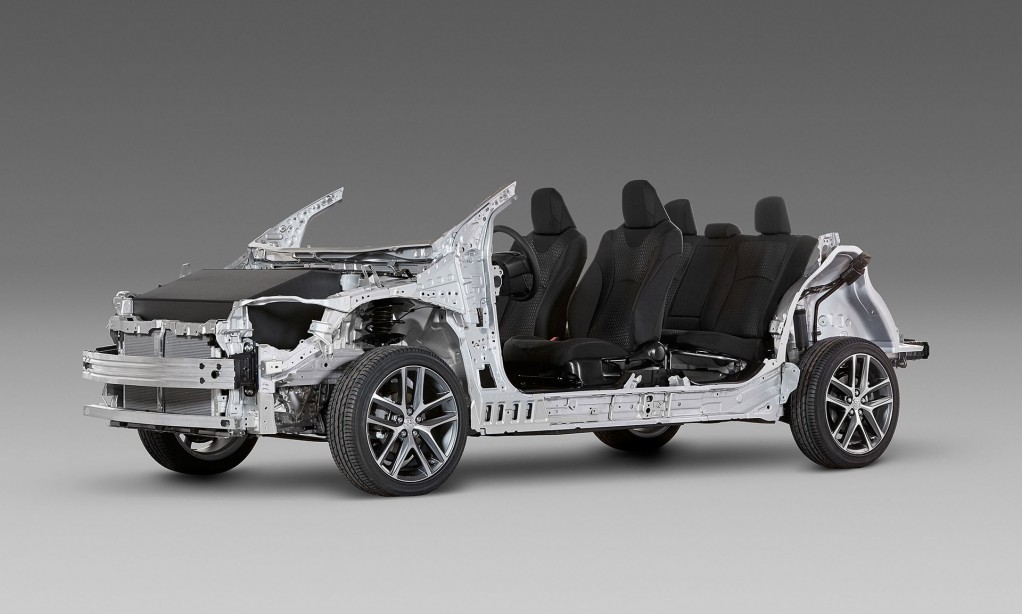
The fourth-generation Prius goes on sale this fall and will be the first to use the Toyota New Global Architecture (TNGA) modular platform. The use of highly flexible, modular platforms in the auto industry is a proven means of speeding up development and reducing costs,
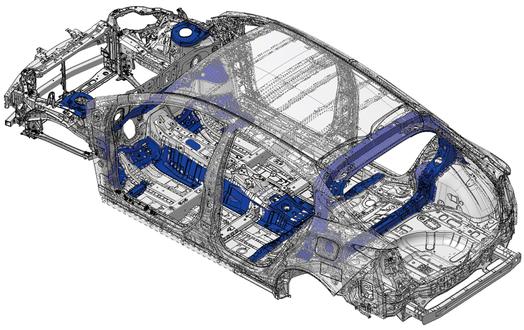
The TNGA uses Laser Screw Welding (with a greater number of weld points), structural adhesives and uniquely shaped frame structures. In addition, the amount of high-tensile strength steel has increased from 3 percent to an impressive 19 percent.
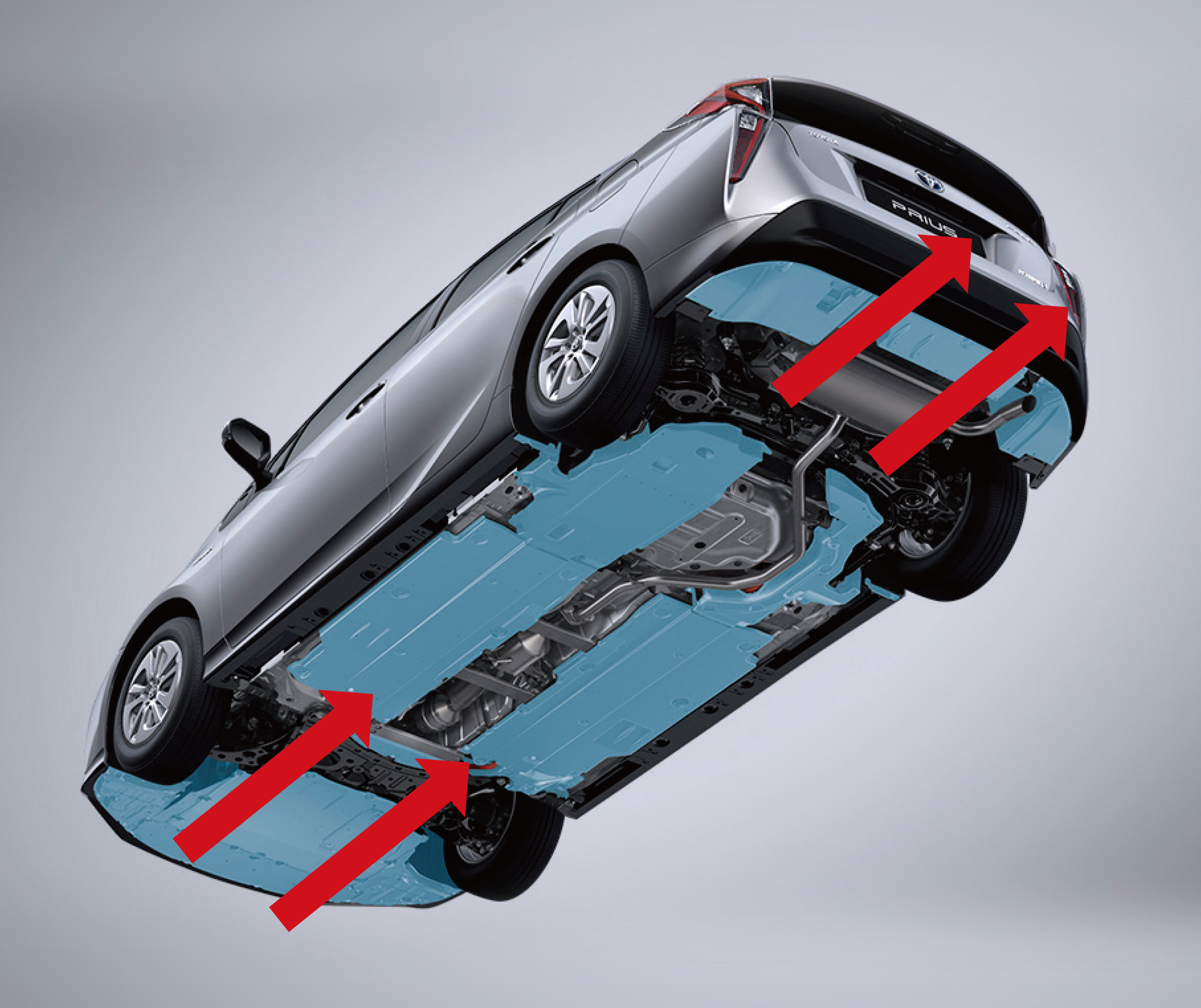
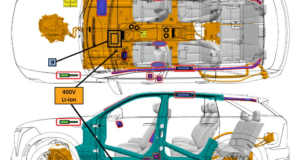
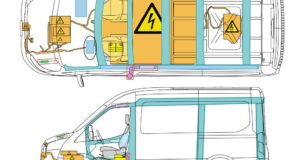
The 2016 Toyota Prius hybrid will offer two battery choices. A nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) battery pack like the one in the old Prius or a lithium-ion option, the same chemistry used in most electric cars and plug-in hybrids. The smaller transaxle and power control unit allow for the auxiliary battery to be installed in the engine compartment.

The 2016 uses a shift-by-wire technology uses electric signals to transmit shift operations and offers light, fingertip operation from the dash-mounted shifter. A “P” position switch provides one-touch engagement of the parking gear. Keep that is mind before you secure the 12 volt battery.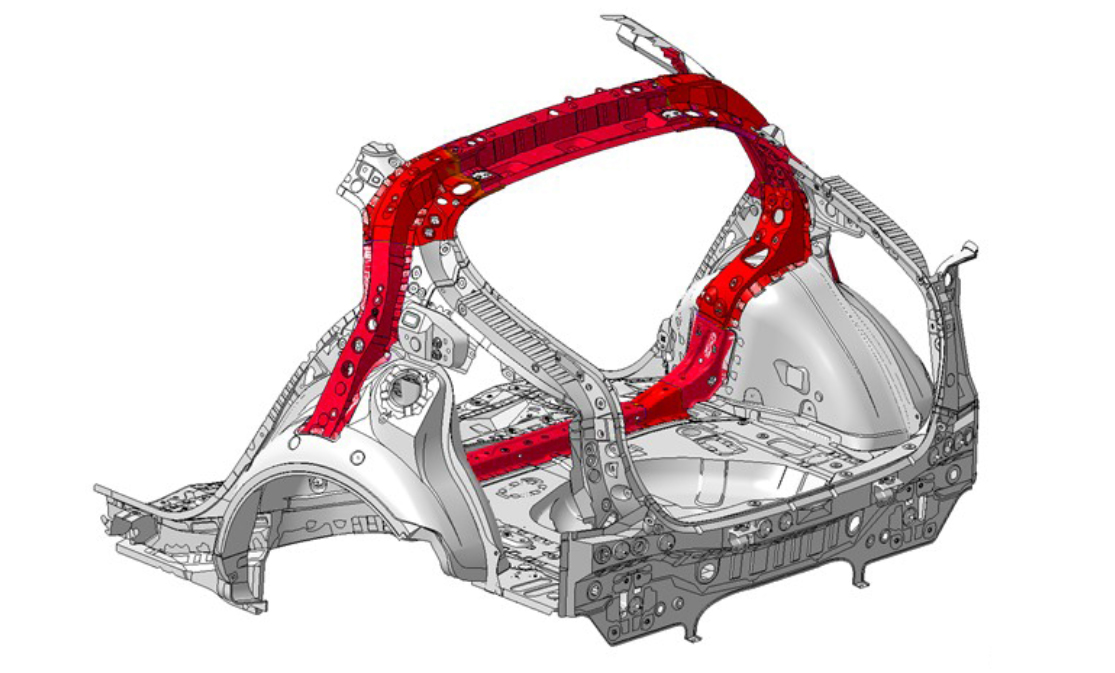
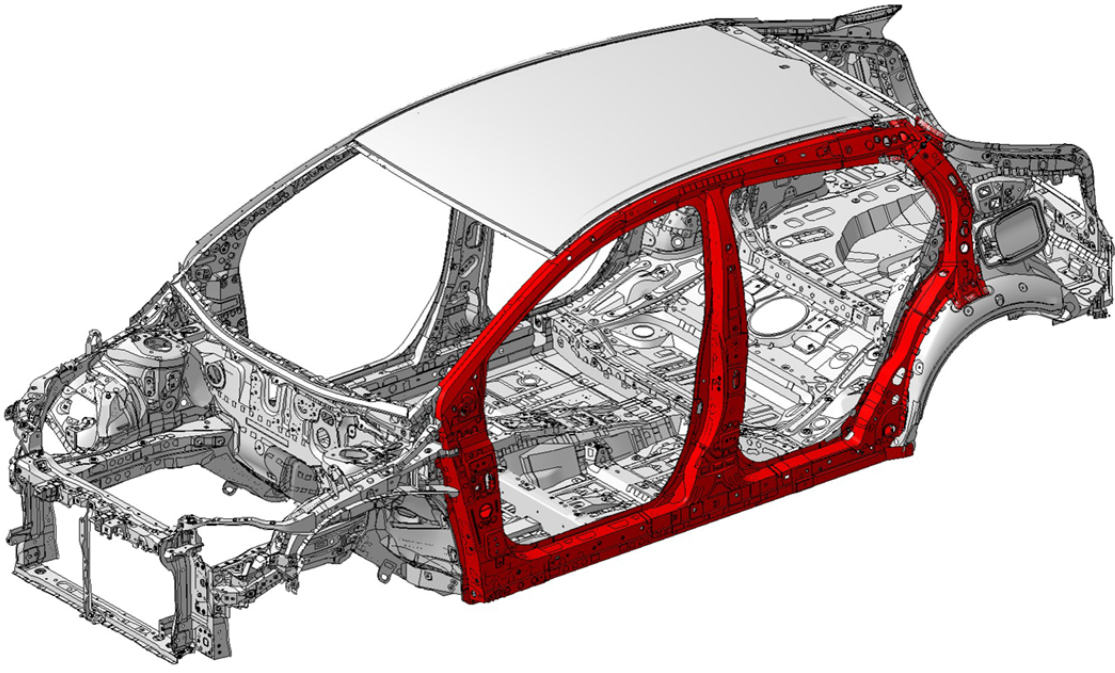
Hot-stamped and high tensile steel, which allows for intricate forms that are both lightweight and strong, is used extensively throughout the new Prius body. More extensive use of aluminum components, including the hood and rear doorframes.
 Boron Extrication An in-depth look into vehicle extrication and rescues involving today's automobiles
Boron Extrication An in-depth look into vehicle extrication and rescues involving today's automobiles